Table of Contents
Security operations (SecOps) is a collaborative approach that integrates security team responsibilities with IT and engineering operations to strengthen an organization’s security posture while maintaining operational efficiency. This methodology bridges the traditional gap between security and operations teams, creating a unified framework that embeds security practices into daily IT operations and the entire development lifecycle. This approach ensures that security is not an afterthought but an integral part of an organization’s operational processes, helping to identify and address threats more efficiently.
This integrated approach combines people, processes, and technology to continuously monitor and improve an organization’s security posture. By embedding security into operations workflows, security teams can detect, investigate, and respond to threats more quickly, minimizing potential damage from incidents. Organizations with well-integrated security and operations functions tend to identify and remediate security issues faster than those with siloed teams, leading to reduced risk exposure and lower remediation costs.
Additionally, this approach typically incorporates a security operations center (SOC), which serves as the central command post for monitoring and analyzing an organization’s security posture. The SOC team is responsible for detecting, investigating, and responding to security incidents across the organization’s infrastructure.
Why security operations matters
The integration of security and operations has become increasingly crucial as organizations face more sophisticated cyber threats and complex IT environments. A unified approach helps organizations maintain operational efficiency while effectively managing security risks.
Implementing integrated security operations practices enables organizations to respond more quickly to security incidents, reducing the potential impact of breaches. This collaborative approach also promotes better communication and coordination between teams, leading to more effective security measures and fewer operational disruptions.
Furthermore, embedding security into operations processes helps organizations maintain compliance with industry regulations and standards. Many regulatory frameworks require continuous monitoring and prompt remediation of security issues, which are core components of this integrated approach.
Key components of security operations
Effective security operations encompass several essential components that form a comprehensive strategy:
Continuous monitoring and detection involves real-time surveillance of networks, systems, and applications to identify potential security threats. This component relies on advanced monitoring tools and technologies that can detect anomalies and suspicious activities across the IT environment.
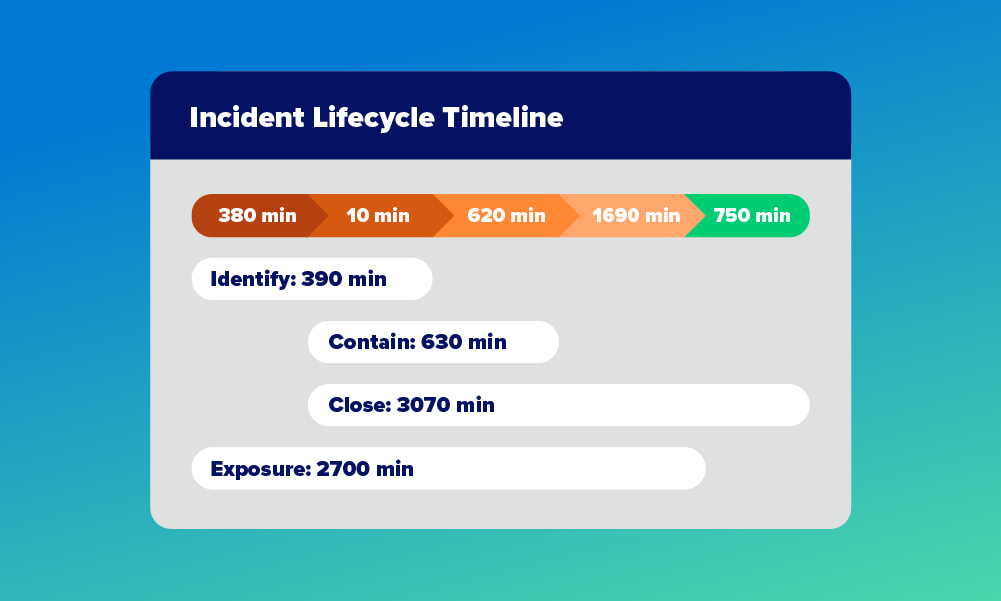
Incident response and management focuses on effectively addressing security incidents when they occur. This includes established procedures for investigating alerts, containing threats, eradicating the root cause, and recovering affected systems.
Vulnerability management entails identifying, classifying, prioritizing, and addressing security vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Regular vulnerability assessments and patch management are crucial aspects of this component.
Threat intelligence integration incorporates up-to-date information about emerging threats and attack techniques into security activities. This intelligence helps organizations proactively defend against new and evolving threats.
Automation and orchestration leverages technology to automate routine security tasks and orchestrate complex response workflows. This automation helps security teams handle large volumes of security data and respond to incidents more efficiently.
Methodologies and frameworks
Several methodologies and frameworks guide the implementation of effective security operations practices:
Development security operations (DevSecOps) extends the principles of DevOps to include security considerations throughout the software development lifecycle. This approach emphasizes “shifting left” by integrating security testing and validation earlier in the development process, reducing the cost and impact of addressing security issues later.
Cloud security operations (CloudSecOps) is the application of security principles to cloud environments, focusing on monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats across cloud infrastructure. It adapts traditional security approaches to address unique cloud challenges while implementing specialized controls and automated workflows to maintain visibility and protect cloud workloads, enabling organizations to securely leverage cloud capabilities.
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) provides a framework for collecting security data from various sources and automating incident response procedures. SOAR platforms help organizations standardize security processes and improve response efficiency.
Security information and event management (SIEM) combines security information management with security event management to provide real-time analysis of security alerts. SIEM systems aggregate and correlate data from multiple sources to help identify potential security incidents.
Information technology infrastructure library (ITIL) offers a set of best practices for IT service management that can be adapted to include security operations. The ITIL framework helps organizations align security operations with broader IT service delivery goals.
Implementation and best practices
Successful implementation of integrated security operations requires careful planning and adherence to best practices:
Cultural alignment involves fostering collaboration between security and operations teams by establishing shared goals and responsibilities. This cultural shift often requires executive support and may involve changes to organizational structure and incentives.
Skills development focuses on ensuring that team members have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively. This includes training in both security principles and operational procedures.
Process integration entails embedding security considerations into existing operational processes rather than treating security as a separate function. This integration helps ensure that security requirements are consistently addressed throughout the organization.
Tool selection and integration involves choosing and implementing tools that support security objectives while integrating with existing systems. The right tools can enhance visibility, automate routine tasks, and improve collaboration between teams.
Metrics and continuous improvement establishes key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring the effectiveness of security practices and identifies opportunities for enhancement. Regular reviews and adjustments help ensure that processes remain effective as threats and technologies evolve.
Challenges and solutions
Organizations implementing integrated security and operations may encounter several challenges:
Skill shortages in cybersecurity continue to affect organizations worldwide. Addressing this challenge may involve investing in training programs, leveraging managed security service providers, or implementing automation to maximize the effectiveness of existing staff.
Tool proliferation can lead to complexity and inefficiency in security operations. Consolidating tools and implementing integrated platforms can help reduce this complexity and improve operational efficiency.
Alert fatigue occurs when security teams are overwhelmed by the volume of alerts generated by security tools. Implementing alert prioritization, automation, and correlation can help teams focus on the most significant threats.
Balancing security and agility requires finding the right approach to securing systems without unnecessarily impeding operations or innovation. Risk-based approaches to security can help organizations allocate resources appropriately based on the potential impact of different threats.
Emerging trends in security operations
The field of security operations continues to evolve in response to changing threats and technologies:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) integration is enhancing the capabilities of security tools by enabling more sophisticated threat detection and automated response mechanisms. These technologies can help identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by traditional rule-based approaches.
Cloud security operations address the unique challenges of securing cloud environments. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, security practices must adapt to monitor and protect resources across multiple cloud platforms and service models.
Extended detection and response (XDR) provides a unified approach to threat detection and response across multiple security layers. XDR platforms integrate data from endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and other sources to provide comprehensive visibility and coordinated response capabilities.
Secure access service edge (SASE) integrates networking and security functions into a unified cloud service, combining SD-WAN with security technologies like Zero Trust controls and firewall services. This architecture provides consistent security and optimized connectivity for users and applications regardless of location, supporting today’s distributed workforce and cloud environments.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) implementation is becoming increasingly important in modern security operations. This security model assumes that threats may exist both outside and inside the network, requiring continuous verification of users and devices regardless of their location.
Alternative approaches
While integrating security with operations provides a comprehensive approach, organizations may consider alternative or complementary models:
Traditional security operations maintain separate security and operations teams with distinct responsibilities. While this approach may be simpler to implement, it often results in slower response times and potential conflicts between security requirements and operational goals.
Managed security services involve outsourcing some or all security operations to specialized providers. This approach can be beneficial for organizations with limited internal security resources or expertise.
Security operations maturity models, such as the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), provide frameworks for assessing and improving security capabilities over time. These models help organizations implement security practices in a phased approach based on their current maturity level.
Compliance-driven approaches focus on meeting specific regulatory requirements rather than implementing comprehensive security operations. While this approach may satisfy immediate compliance needs, it often leaves gaps in addressing emerging threats and security challenges.
Conclusion
The integration of security and operations has become an essential approach for organizations seeking to maintain effective security while supporting operational efficiency and business innovation. By bringing together these functions, organizations can respond more quickly to threats, reduce the impact of security incidents, and build more resilient systems.
As cyber threats continue to evolve in sophistication and impact, the collaboration and coordination fostered by integrated security practices will become increasingly valuable. Organizations that successfully implement this approach can not only improve their security posture, but also enhance their ability to deliver services and drive innovation in an increasingly complex and challenging environment.
SecOps assessment tools from Expel
Organizations can leverage various assessment tools and resources to effectively implement security operations practices. Self-assessment tools and SecOps solutions and maturity models enable security teams to evaluate their current capabilities, set improvement targets, and track progress across key functional areas. These tools typically provide visualization capabilities that help communicate program maturity to stakeholders and guide resource allocation decisions. By incorporating regular security operations assessments into their security programs, organizations can systematically measure their capabilities, identify gaps, and demonstrate continuous improvement in their security posture. Find Expel’s SOC assessment tools here.