Table of Contents
Auto remediation is a cybersecurity capability that automatically executes predefined response actions to address security incidents, vulnerabilities, and compliance violations without manual intervention. Auto remediation combines advanced detection technologies with programmatic response workflows to neutralize threats at machine speed. This dramatically reduces response times from hours to minutes while minimizing human error and operational burden on security teams.
Why is auto remediation important?
A recent IBM study found that the average time to identify and contain a data breach is 277 days. The average cost per incident reaches $4.45 million. Auto remediation addresses this critical gap by enabling organizations to respond to threats within minutes rather than hours or days.
As Claire Hogan, Principal Product Manager of Analyst Efficiency at Expel, explains: “Cyber attacks move faster than human analysts can respond, and reducing attacker dwell time is a critical benefit that automation provides to organizations. Automation allows for real-time detection and response before threats can escalate.”
Security teams today face an overwhelming volume of alerts. The average enterprise receives over 11,000 security alerts per month. This alert fatigue, combined with the global cybersecurity skills shortage, makes automated remediation essential for maintaining effective security operations.
What are the main challenges that auto remediation addresses?
Modern security operations face numerous challenges that make auto remediation essential for effective cybersecurity management.
Alert fatigue and volume
According to Claire Hogan, auto remediation becomes critical because “security teams are flooded with alerts daily, and automation helps triage and prioritize threats while reducing alert fatigue. This allows your human analysts to focus on what matters most.”
Speed and consistency challenges
Cyber attacks now unfold in minutes, not hours. Manual incident response processes are susceptible to mistakes, especially during high-stress situations. Claire Hogan emphasizes: “Automated systems follow set rules and logic, whereas humans are prone to error, especially when alert fatigue sets in. Automation reduces the chance of human error. It ensures consistent responses across all incidents.”
Resource constraints
The cybersecurity industry faces a critical skills shortage. Auto remediation helps organizations maximize the impact of their existing security teams by automating routine response tasks. As Hogan notes, automation enables organizations to “save time and money while reducing the manual burden of alerts and repetitive tasks for security teams.”
How does auto remediation work?
Auto remediation systems utilize several interconnected components to detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents automatically.
Automated response playbooks
At the heart of any auto remediation system are predefined playbooks. These specify exact response procedures for different types of incidents. The playbooks incorporate decision trees, conditional logic, and sequential actions that mirror expert human response processes.
Security orchestration and integration
Modern automated remediation relies on security orchestration platforms that integrate with multiple security tools simultaneously through APIs. This enables coordinated responses across firewalls, endpoint protection systems, identity management platforms, cloud infrastructure, and email systems.
Intelligent policy engines
Advanced auto remediation systems use policy engines that make contextual decisions. These decisions are based on threat intelligence, asset criticality, user roles, and business impact. This ensures appropriate responses for specific situations and organizational context.
Common auto remediation use cases
Endpoint security automation
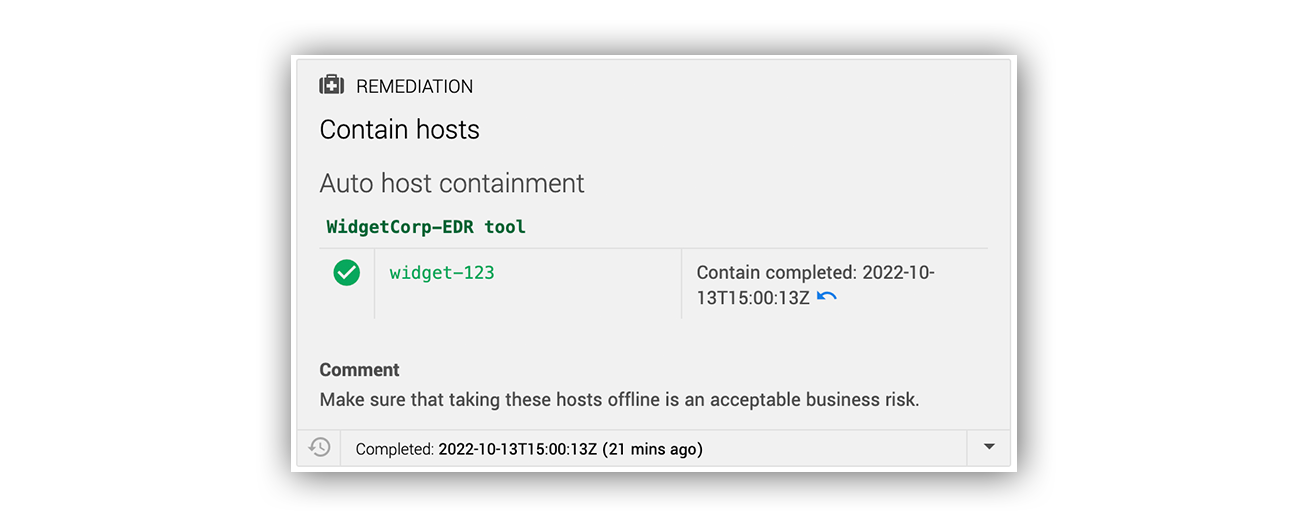
A compelling example comes from Claire Hogan at Expel, who describes their automated process termination capability: “Automated process termination might seem like a small action because it’s lightweight—no system isolation or user disruption is involved. But it can be highly impactful. It saves time and prevents malware from spreading or escalating like ransomware encrypting files. It eliminates the need for manual intervention on every detection. It reduces the total number of incidents requiring escalation by cutting them off early.”
This demonstrates how seemingly simple auto remediation actions can have compound effects—stopping a single malicious process can prevent an entire incident from escalating.
Here’s an example of an Expel “contain host” auto remediation:
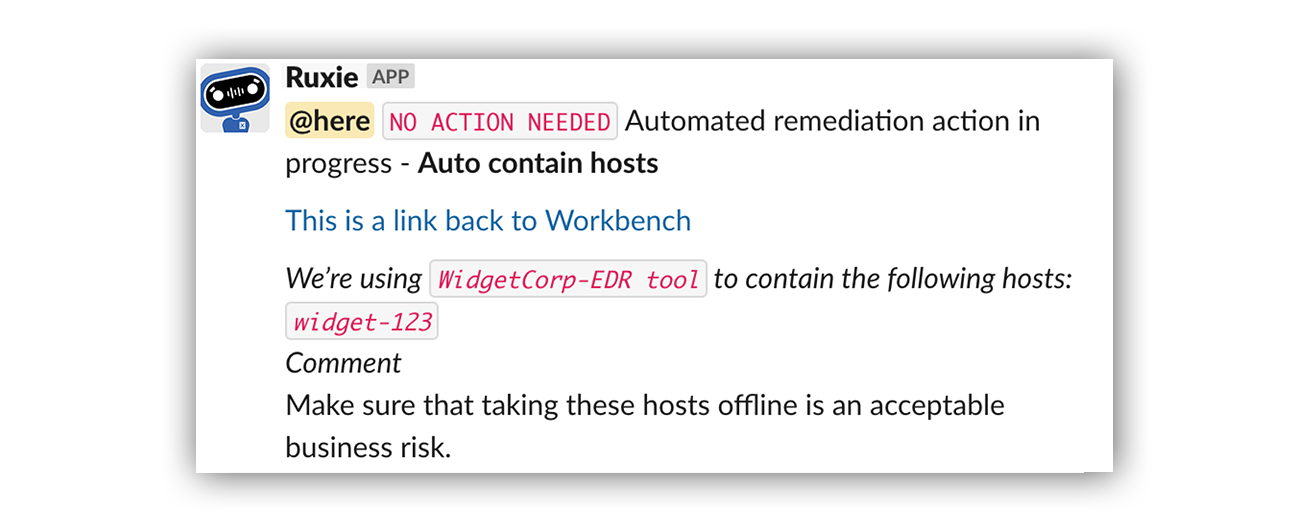
… And how that alert looks in Slack.
Identity and access management
Identity-focused automated remediation includes disabling compromised user accounts, resetting passwords for breached credentials, and adjusting user permissions. These actions are based on risk scores and threat indicators.
Email and network security
Auto remediation can automatically remove phishing emails from user inboxes. It can block malicious IP addresses and domains, update firewall rules, and isolate network segments. These actions prevent threat propagation across the network.
How can organizations build trust in automated remediation?
Trust is paramount when implementing auto remediation in high-stakes security environments. Claire Hogan identifies four key approaches: “Building trust in automation requires transparency, keeping humans in the loop, thorough testing, and granular controls built into how you execute automation.”
Transparency and human oversight
Organizations need clear visibility into what automated remediation systems are doing and why. As Hogan explains: “You want to ensure your team has complete visibility into what the automation is doing and why. Clear rule-based logic, explainable permissions, and transparent decision paths help build confidence.” Effective systems maintain human decision-making authority while automating execution. As Hogan notes: “Keeping the decision to automate controlled by humans helps calibrate trust over time—there’s always a human triggering each automated action.” This approach ensures systems don’t make independent decisions.
Testing and granular controls
Before deploying automatic remediation in production environments, organizations must validate system behavior through rigorous testing. Teams should be able to “set clear thresholds and scopes for automation so it doesn’t feel like a black box,” as Hogan describes.
Implementation best practices
Successful auto remediation implementation requires careful planning and customization. As Claire Hogan emphasizes: “Automation is definitely not a one size fits all type of thing.” It must be tailored to work effectively in each environment.
Organizations should start with low-risk, high-volume use cases. They should develop comprehensive testing procedures and implement robust governance frameworks. This approach aligns with NIST incident response guidelines for systematic threat management.
Measuring success and impact
Organizations can measure auto remediation effectiveness through both quantitative and qualitative metrics. According to Claire Hogan, “You can accurately measure the impact of auto remediation on your team’s productivity and burnout by using a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures.”
Key metrics include Mean Time to Response (MTTR) reduction, ticket closure rates, and analyst satisfaction. As Hogan concludes: “Automation isn’t just a tech upgrade—it’s really an investment in both your people and your security as a company.”
How Expel does auto remediation
Expel’s auto remediation solution connects detection directly to action with 24×7 coverage. According to Claire Hogan: “Auto remediation enables Expel to automate specific response capabilities within your systems so that attacks can be rapidly contained without requiring intervention from you.”
A critical aspect of Expel’s approach is maintaining human control: “Our analysts create and assign all remediation actions in Workbench, but the actions themselves are carried out within your specific vendor technologies. We automate the remediation action itself, but not the decision to remediate.”
Our approach to automated remediation is customized to your organization. It’s based on the frequency of threats in your environment. You control which users and endpoints we can take offline immediately after compromise confirmation. This enables your team to focus on strategic security initiatives.
Related auto remediation resources
Explore more about auto remediation and automated security response: