Table of Contents
When you’re evaluating managed detection and response (MDR) services, one of the first questions you’ll ask is: what exactly can MDR monitor? The answer matters because comprehensive coverage across your technology stack is essential to detecting and responding to threats effectively. Most MDR services monitor endpoints, cloud workloads, Kubernetes containers, SaaS applications, network traffic, email security, identity systems, and SIEM logs—but the depth and breadth of coverage can vary significantly between providers.
What does MDR monitor?
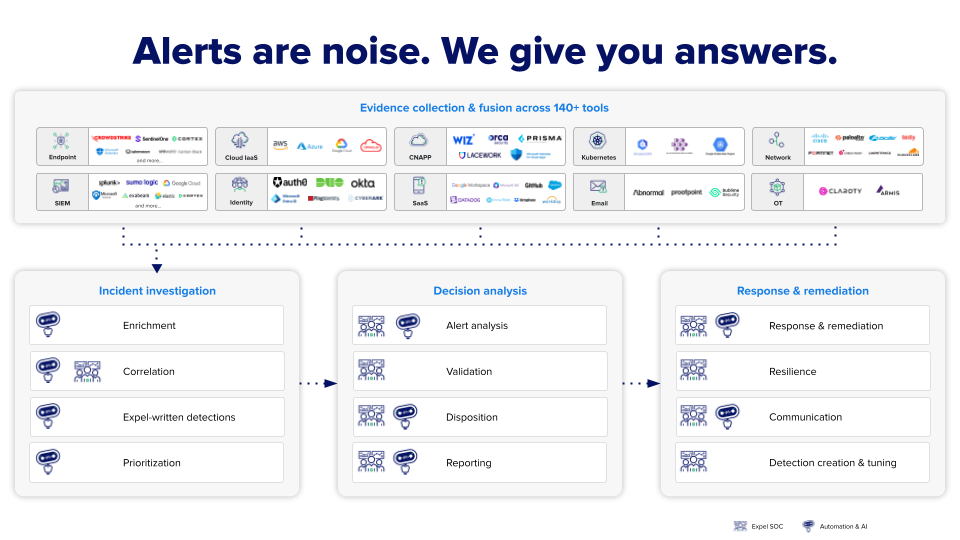
MDR monitors your entire technology environment to detect and respond to threats across multiple attack surfaces. Rather than focusing on just one area of your security infrastructure, effective MDR provides visibility into everything from individual devices to cloud workloads to user identities.
According to Expel’s approach to MDR, the service “quickly detects advanced threats across your tech (endpoint, cloud, Kubernetes, SaaS, network, SIEM, email, identity, and more).” This comprehensive monitoring strategy means security analysts can correlate suspicious activity across different systems—for example, connecting unusual endpoint behavior with suspicious cloud API calls and abnormal identity activity to identify sophisticated multi-stage attacks.
The technology monitoring typically includes:
Endpoints and devices: MDR integrates with endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to monitor laptops, desktops, servers, and mobile devices. This includes tracking processes, registry changes, file system activity, and network connections on monitored endpoints. As Expel’s endpoint security monitoring explains, MDR enhances your EDR/XDR tools by applying behavioral detections designed to spot sophisticated activity vendor alerts alone might miss.
Cloud infrastructure: MDR provides visibility into cloud control planes across major platforms including AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). This monitoring detects threats like privilege abuse, API misuse, unauthorized access, and suspicious configuration changes. Expel’s cloud detection and response services offer coverage across cloud workloads, cloud control services, and Kubernetes infrastructures for comprehensive cloud protection.
Network activity: MDR monitors network traffic to detect malicious and suspicious activity coming to and going from all devices connected to the network. Network detection capabilities help identify lateral movement, data exfiltration attempts, command and control communications, and other network-based threats.
Identity and access management: MDR integrates with identity platforms like Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), Okta, and Duo to detect unauthorized access, credential misuse, suspicious logins, privilege escalations, and anomalous authentication patterns. Identity-based monitoring has become increasingly critical—Expel’s 2025 Annual Threat Report found identity-based incidents made up 68% of all incidents among Expel customers.
Email security: MDR monitors email platforms to detect and respond to email-based threats including phishing attempts, malicious attachments, suspicious links, and business email compromise (BEC) attacks. According to Expel’s email security services, this includes 24×7 detection, investigation, and response of email-based threats with innovative detection strategies built specifically for email environments.
SaaS applications: MDR provides security coverage for critical SaaS applications by monitoring user behavior, data movement, authentication patterns, and API usage. Expel’s SaaS security monitoring integrates directly with SaaS applications to build high-fidelity detections that identify data exfiltration, unusual login patterns, excessive downloads of personally identifiable information (PII), and unauthorized access to sensitive files.
SIEM and security logs: MDR leverages security information and event management (SIEM) systems to analyze logs from network devices, security appliances, operating systems, and applications. As noted in Expel’s SIEM guide, SIEM platforms collect data from endpoints, network devices, servers, applications, and other security tools to provide comprehensive visibility.
What technologies are covered by managed detection and response?
Managed detection and response coverage extends across your entire technology ecosystem, with most MDR services monitoring eight core technology categories:
Endpoints: MDR covers traditional endpoints including Windows and Mac computers, Linux servers, virtual machines, and mobile devices. This monitoring relies on EDR agents that collect detailed telemetry about system behavior, processes, and network activity. Expel’s MDR approach integrates with leading EDR/XDR platforms like CrowdStrike, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, SentinelOne, and Carbon Black.
Cloud workloads: Cloud workload monitoring encompasses virtual machines, containers, serverless functions, and cloud-native applications running across multi-cloud environments. MDR detects threats in cloud workloads including malware infections, crypto-mining activities, unauthorized access, and suspicious process execution. The monitoring extends to both infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) deployments.
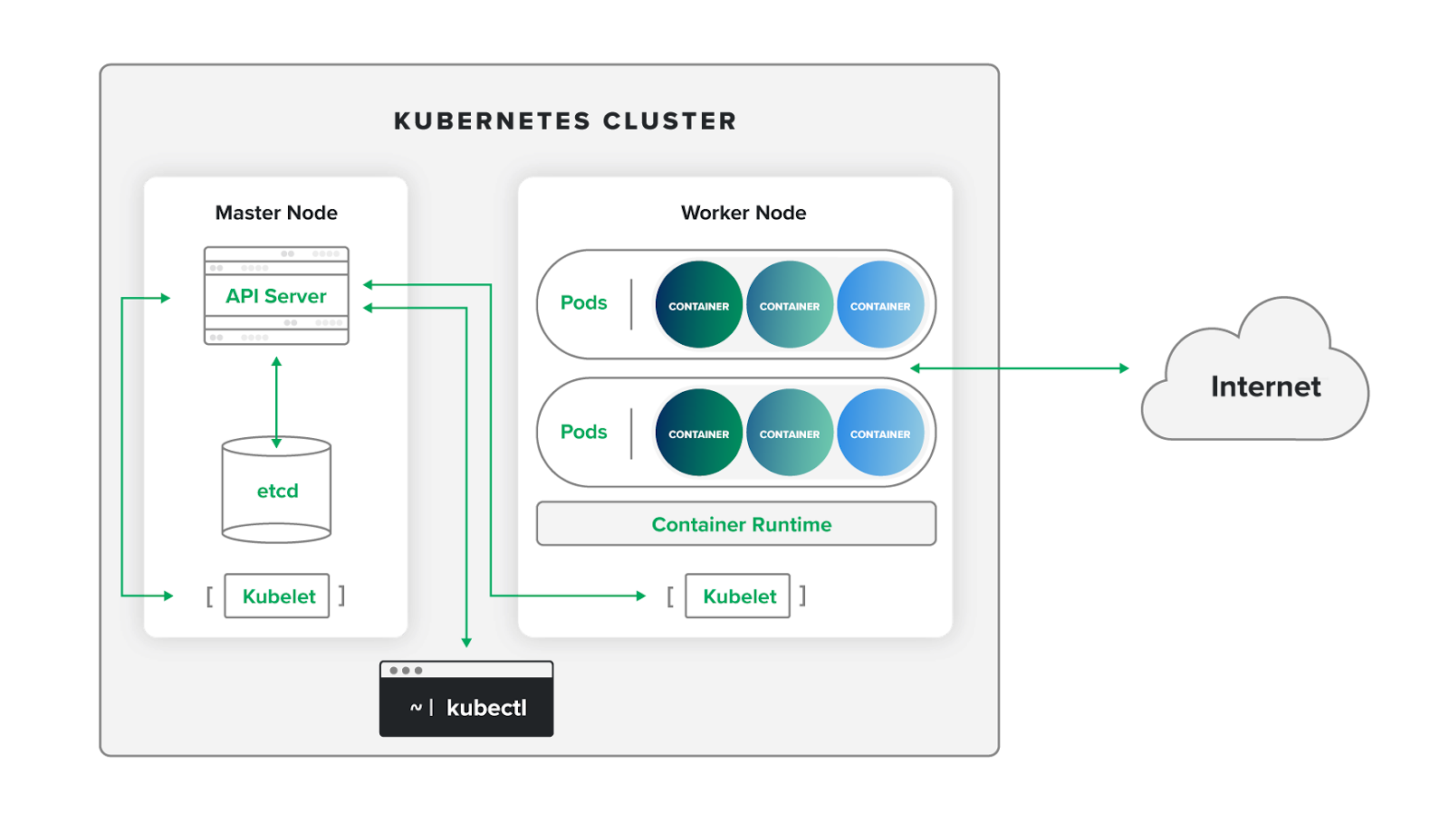
Kubernetes containers: Container orchestration platforms require specialized monitoring capabilities. According to Expel’s Kubernetes security guidance, MDR for Kubernetes monitors clusters running on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). The monitoring analyzes Kubernetes audit logs to detect events like anonymous API access, privilege escalation through role bindings, and suspicious container deployments.
SaaS applications: MDR monitors business-critical SaaS platforms including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, GitHub, and other cloud applications. SaaS security monitoring focuses on threat detection by analyzing user behavior, data movement, authentication patterns, and API usage to identify security breaches or data theft attempts.
Network infrastructure: Network monitoring covers firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), VPNs, routers, switches, and network access control (NAC) systems. This technology layer helps detect suspicious traffic patterns, unauthorized network access, lateral movement, and command and control communications.
Email platforms: Email security coverage includes Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and third-party email security gateways. MDR monitors for phishing campaigns, malicious attachments, suspicious sender behaviors, email forwarding rules, and business email compromise attempts.
Identity systems: Identity platform monitoring covers single sign-on (SSO) providers, multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems, directory services, and privileged access management (PAM) solutions. This includes platforms like Okta, Microsoft Entra ID, Duo, and Ping Identity.
SIEM platforms: MDR integrates with SIEM solutions like Splunk, Microsoft Sentinel, Sumo Logic, and others to access aggregated log data and security events across the environment. Expel’s SIEM strategy enhances SIEM capabilities by applying custom detection logic and providing 24×7 monitoring and response.
Does MDR work with cloud environments?
Yes, MDR works extensively with cloud environments and provides some of the most critical security monitoring capabilities for cloud infrastructure. As organizations accelerate cloud adoption, cloud security has become a primary focus area for modern MDR services.
Expel’s cloud detection and response provides comprehensive cloud coverage extending from the application layer to the cloud control plane. This means MDR monitors both what’s running in your cloud (workloads, containers, applications) and how your cloud is configured and accessed (control plane APIs, identity and access management, configuration settings).
Cloud environment monitoring includes:
Multi-cloud infrastructure: MDR supports monitoring across AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. This multi-cloud coverage is essential as 91% of enterprises use multiple cloud providers. The monitoring detects suspicious API calls, unusual resource provisioning, unauthorized access attempts, and configuration changes that could introduce security risks.
Cloud-native applications: MDR monitors serverless functions (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions), container platforms, and cloud-native databases. This application-level monitoring identifies threats like code injection, unauthorized function execution, and suspicious database queries.
Cloud control plane: The control plane represents the management layer of your cloud infrastructure where administrators configure resources, manage identities, and define policies. Expel’s approach includes monitoring cloud control plane activities to detect privilege escalation, suspicious role assumption, policy modifications, and unauthorized resource access.
Cloud security posture management: MDR analyzes cloud configurations to identify misconfigurations, overly permissive policies, and compliance violations. This proactive monitoring helps prevent security incidents before they occur.
Cloud workload protection: MDR integrates with cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs) and cloud-native application protection platforms (CNAPPs) to provide runtime protection for virtual machines, containers, and serverless workloads. According to Expel’s Wiz integration announcement, this includes leveraging specialized runtime security rules designed to spot suspicious behavior and live threats in cloud environments.
The effectiveness of cloud MDR depends on deep integration with cloud platforms. Rather than relying solely on generic alerts from cloud providers, leading MDR services write custom detections tailored to cloud-specific threats. Expel’s cloud security approach includes custom Expel-written detection rules that detect 98% of cloud incidents in their security operations center.
Can MDR monitor Kubernetes?
Yes, MDR can monitor Kubernetes environments, and specialized Kubernetes monitoring has become increasingly important as container adoption accelerates. However, Kubernetes security presents unique challenges requiring purpose-built detection capabilities.
According to Expel’s Kubernetes security research, 55% of DevOps, engineering, and security teams have delayed applications because of Kubernetes security concerns, and 93% experienced at least one security incident in their Kubernetes environments in the past year. This highlights the critical need for effective Kubernetes monitoring.
MDR for Kubernetes provides several key capabilities:
Audit log analysis: Kubernetes audit logs capture detailed information about API server requests, including user identities, resources accessed, and operations performed. MDR analyzes these logs to detect suspicious activities like anonymous API access, privilege escalation attempts, and unauthorized resource modifications. As outlined in Expel’s Kubernetes event monitoring guide, security teams should watch for events like publicly accessible API endpoints, default service account privilege escalations, and suspicious container image deployments.
Container runtime monitoring: MDR monitors containers during runtime to detect malicious processes, crypto-mining activities, suspicious network connections, and attempts to escape container boundaries. This runtime visibility helps identify threats that may evade static security scanning.
Kubernetes-specific detections: Generic security tools often generate excessive false positives in Kubernetes environments due to the dynamic nature of container orchestration. Purpose-built MDR solutions apply Kubernetes-specific detection logic accounts for normal cluster behavior while identifying genuine threats. Expel’s Kubernetes detections are designed to adapt and learn from cluster activity while aligning to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Multi-cluster visibility: Many organizations run multiple Kubernetes clusters across different environments (development, staging, production) and cloud providers (EKS, GKE, AKS). MDR provides centralized visibility across all clusters to detect suspicious patterns and ensure consistent security coverage.
Integration with container security tools: MDR integrates with container security platforms like Prisma Cloud, Lacework, and CrowdStrike to enhance detection capabilities. According to Expel’s Kubernetes security approach, this integration allows security teams to get more value from existing container security investments.
The complexity of Kubernetes environments makes them particularly challenging for security teams. As noted in Expel’s Kubernetes fundamentals guide, Kubernetes generates tremendous volumes of alerts due to constant container creation and destruction, interconnected components, and lack of application-specific context. MDR addresses these challenges by filtering noise, providing context, and delivering actionable security findings rather than raw alerts.
MDR technology coverage
The breadth and depth of MDR technology coverage directly impacts your security effectiveness. Comprehensive coverage means fewer blind spots where attackers can operate undetected, while shallow coverage creates gaps sophisticated adversaries will exploit.
Modern MDR services provide coverage across multiple dimensions:
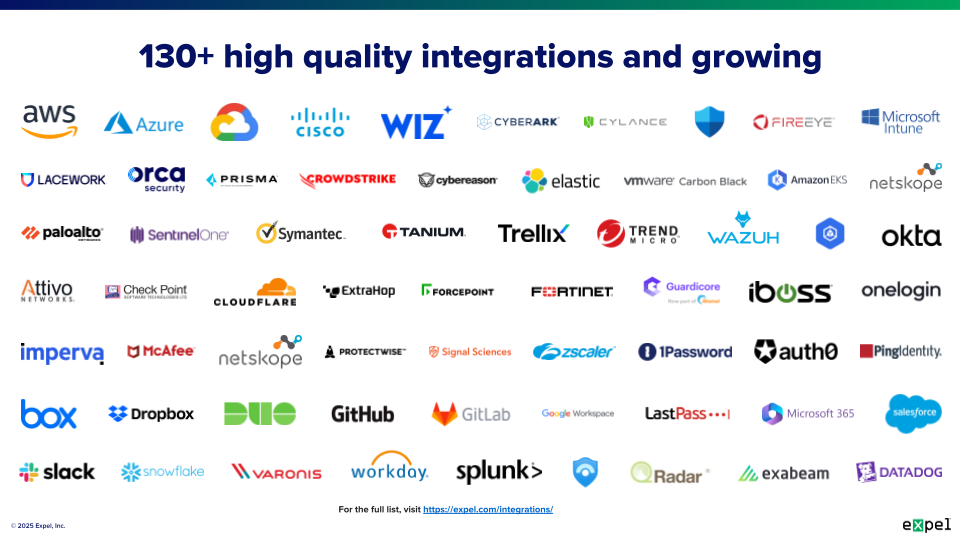
Platform breadth: Leading MDR providers integrate with 100+ security technologies. Expel’s MDR platform includes 130+ integrations across endpoint, cloud, Kubernetes, SaaS, network, SIEM, email, and identity technologies. This extensive integration ecosystem allows organizations to leverage their existing security investments while gaining expert monitoring and response capabilities.
Attack surface completeness: Effective MDR monitors all major attack surfaces including:
- Traditional on-premises infrastructure (endpoints, servers, network devices)
- Cloud infrastructure and workloads (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud)
- Container platforms (Kubernetes, Docker)
- SaaS applications (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, GitHub)
- Email systems (Exchange, Office 365, Gmail)
- Identity platforms (Okta, Microsoft Entra ID, Duo)
- Development environments (code repositories, CI/CD pipelines)
Detection methodology: Technology coverage extends beyond simple alert monitoring. According to what makes good MDR, effective services implement real-time monitoring, automated detection systems, predefined playbooks, and automated remediation capabilities. This includes:
- Vendor-native detections from security tools
- Custom MDR provider detections written by security experts
- Behavioral analytics to identify anomalous activity
- Threat intelligence integration for known indicators of compromise
- Cross-product correlation to detect sophisticated multi-stage attacks
Hybrid environment support: Most organizations operate hybrid environments with a mix of on-premises infrastructure, multiple cloud providers, and SaaS applications. MDR technology coverage must span these diverse environments. Expel’s approach emphasizes “complete coverage using tools you already have,” allowing organizations to maintain their existing technology stack while gaining comprehensive security monitoring.
Specialized environments: Beyond standard IT infrastructure, some organizations require monitoring for specialized environments including:
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices in operational environments
- Operational technology (OT) systems in manufacturing and industrial settings
- Medical devices in healthcare environments
- Point-of-sale systems in retail environments
The key differentiator between MDR providers often comes down to detection depth rather than just technology breadth. As Expel’s cloud security page notes, “Expel was the only vendor we evaluated that wrote its own meaningful cloud detections, and weren’t just a proxy for GuardDuty.” This highlights the importance of custom detection logic beyond simply forwarding alerts from security tools.
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between endpoint monitoring and full MDR coverage? Endpoint monitoring focuses specifically on devices like laptops, desktops, and servers through EDR tools. Full MDR coverage extends beyond endpoints to monitor cloud infrastructure, SaaS applications, network traffic, identity systems, email, and more. This comprehensive approach allows security analysts to correlate suspicious activity across your entire technology stack to detect sophisticated multi-stage attacks endpoint-only monitoring would miss.
Can MDR integrate with the security tools we already have? Yes, modern MDR services are designed to work with your existing security technology stack. Rather than requiring you to replace current tools, MDR integrates with your EDR platforms, cloud security tools, SIEM systems, identity providers, and other security solutions through APIs and other connection methods. Expel’s integration portfolio includes 130+ technologies, and most leading MDR providers support similar breadth of integrations.
How does MDR handle multi-cloud environments? MDR monitors multi-cloud environments by integrating with each cloud platform’s security services and APIs. This includes AWS CloudTrail, Azure Security Center, Google Cloud Security Command Center, and Oracle Cloud Guard. The MDR service normalizes alerts and telemetry from different cloud providers into a unified view, applies consistent detection logic across all platforms, and correlates suspicious activity between clouds to identify threats spanning multiple environments.
Does MDR require deploying agents across our infrastructure? It depends on the MDR provider and the technologies being monitored. Some MDR services, like Expel, connect to most security tools through API integrations without requiring additional agents. However, endpoint monitoring typically does require EDR agents on devices. Cloud, SaaS, identity, and network monitoring generally use agentless API-based integrations. The trend in MDR is toward agentless monitoring where possible to reduce deployment complexity and management overhead.
What happens if we add new technologies to our environment? Leading MDR services support unlimited technology integrations, allowing you to add new security tools, cloud platforms, SaaS applications, or other technologies without additional costs or complex reconfigurations. The MDR provider integrates the new technology into their monitoring platform and applies relevant detection logic. According to Expel, their Premium tier includes “unlimited technology integrations,” allowing the service to grow with your evolving technology stack.